After years of harsh critiques from environmental groups and departing co-op members over its slow pace of change, Tri-State Generation is now winning praise for plugging in and planning a host of solar and wind farms to replace dirty coal.
The Westminster-based utility serving a million consumers through co-ops in four Western states will link to hundreds of megawatts of new solar power by the end of 2025. Its newest five-year building plan was unopposed when filed with state regulators, and wins praise from environmentalists for a wide array of new wind farms and innovative battery storage solutions.
The big utility, meanwhile, is making it easier for disgruntled member co-ops to accelerate renewable projects they build for themselves outside the Tri-State grid, in one effort to head off more defections like those that turned United Power and Delta-Montrose Electric Association into independents.
Tri-State is even throwing a technically advanced green wild card into its future studies, saying it will consider an innovative geothermal electricity project in Colorado while seeking “dispatchable” or always-on backup power sources. Before now, most such “dispatch” power fill-ins by other utilities included new natural gas turbines, which emit less greenhouse gas than coal but are still controversial among renewable energy advocates.
☀️ READ MORE
The utility has its eye on hundreds of millions of dollars in federal Inflation Reduction Act subsidies, and if it succeeds, will be well on its way to achieving an 89% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, ahead of state targets. The utility is also getting credit for recent agreements to spend big in supporting economic development in Western Slope communities where it is closing coal plants, which are large employers and vital money engines in small towns.
“Tri-State should be commended for aggressively pursuing federal funding to support its plan to retire existing coal units and acquire new renewable generation and storage resources,” Clare Valentine, senior policy advisor at the renewable resources nonprofit Western Resource Advocates, said, “all in a way that maintains reliability and delivers climate and economic benefits to member cooperatives and communities.”
Tri-State’s resource plan for how it will generate power from 2026 to 2031 was filed as an unopposed “settlement” with the Colorado Public Utilities Commission, giving it every chance at approval. Now Tri-State will start seeking bids on the projects in its resource plan, and see which ones make economic sense after lucrative federal subsidies are factored in.
As a nonprofit co-op utility, Tri-State did not qualify for federal tax credits that can amount to hundreds of millions of dollars until a recent rule change. With the change, and the continuing drop in long-term costs to build solar and wind generation, Tri-State can build renewable replacements without blowing up prices for its co-op members, vice president of communications Lee Boughey said.
Tri-State’s five-year resource plan filed with the PUC starts with construction of a large lithium-ion battery array in New Mexico in 2026, along with a smaller iron-air battery test in eastern Colorado. The advantage of iron-air batteries is they can hold up to 100 hours of backup power, while current battery arrays hold about four hours. Powdered iron rust is charged with generated electricity, turning it back into metallic iron. Exposed to oxygen, the iron rusts again, releasing a steady electrical current that can be sent out on the grid, all employing cheap, environmentally friendly materials.
The five-year plan also includes a new 140 megawatt solar farm in western Colorado in 2026, and another in New Mexico in 2029. Much of the rest is wind, with five new wind farms proposed to go online between 2026 and 2031 in Wyoming and western Nebraska, eastern Colorado and New Mexico.
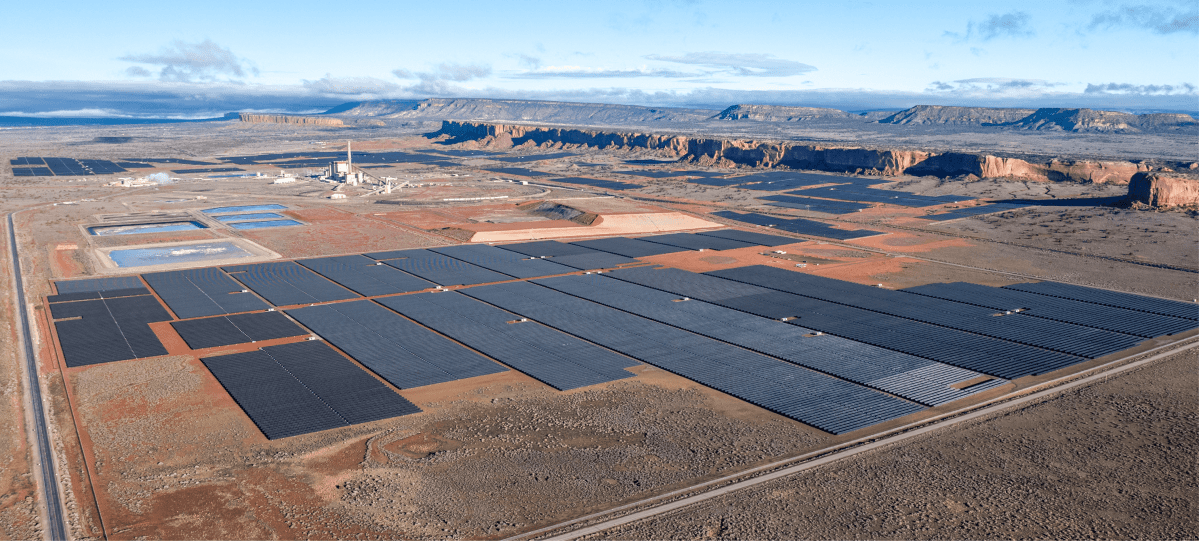
Those are in addition to large solar hookups that are part of Tri-State’s current five-year plan, including 595MW of solar already online in 2024 and finishing up by late 2025. Symbolic of Tri-State’s rapid transition, Boughey said, is the new solar farm that surrounds a closed Tri-State coal-fired plant in New Mexico.
The schedule for bringing renewable energy online will allow Tri-State to stick to its current schedule of closing coal-fired Craig Unit 1 by the end of 2025, which it co-owns with other utilities; Unit 2 in late 2028; and solely owned Unit 3 on Jan. 1, 2028. Tri-State also plans to close the large 458MW Springerville, Arizona, Unit 3 in 2031.
The change in the mix would mean that by 2030, 70% of the co-op members’ energy mix will be from clean sources, Tri-State said. In that same year, Tri-State would have reduced greenhouse gas emissions from electrical generation by 89% from the state’s 2005 baseline, the association said.